Monocots |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
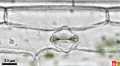
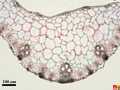
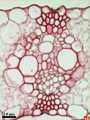
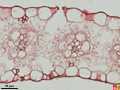
Monocotyledonous leaves show a parallel venation and mostly are arrow or band-shaped. Stomata and other epidermal cells are almost always arranged in parallel arrays. These characterics are depicted in the photographs below of maize, papyrus and yucca. How monocotyle leaves develop is further explained in the section on monocot leaf formation.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||